By Carole Excell and Stephanie Ratte (Posted: November 20, 2014)
Portland Bight (PBPA) is Jamaica’s largest protected area, extending more than 200 square miles of land and 524 miles of sea. The region is home to 30,000 acres of mangroves, four dry limestone forests, and several threatened species, including the critically endangered Jamaica Iguana. But last year, the Jamaican government revealed plans to lease Goat Islands, two cays located in the protected area, to China Harbour Engineering Company (CHEC) to develop a sprawling $1.5 billion trans-shipment port. The project is expected to flatten the Goat Islands and dredge sizable areas, impacting fishing, tourism, biodiversity, and coastal resilience. What’s also troubling is that the government has released scant information about the project, preventing citizens from learning about how the port may impact them or voicing their concerns at an early stage of development.
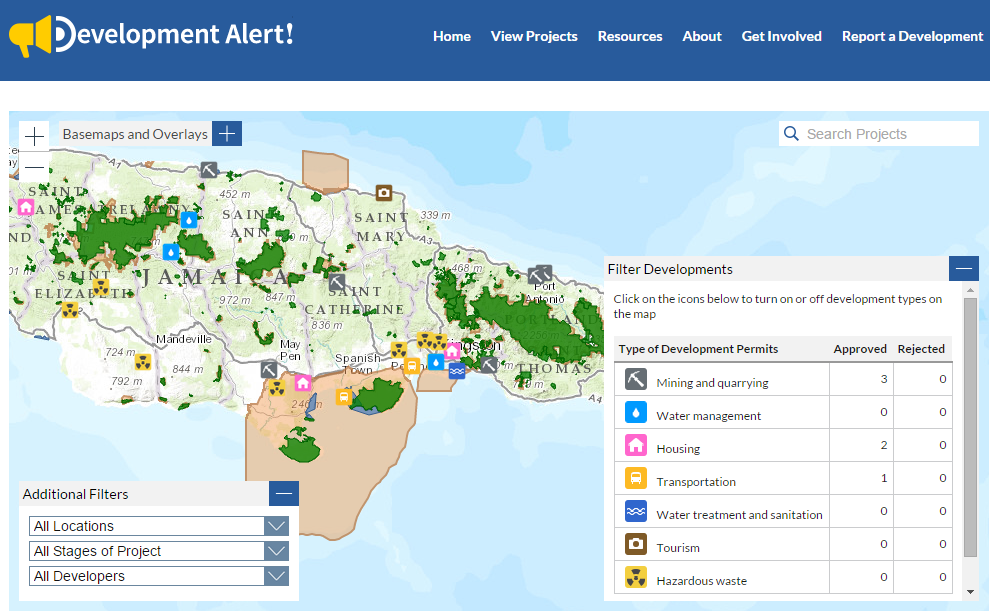
This is not an isolated incident: Like many governments, Jamaica does not proactively disclose applications at an early stage for development projects like shipping ports, highways, housing developments, and more. What information is released—such as environmental impact assessments—is presented in a format that’s difficult for citizens to access and understand. Enter Development Alert!: The new tool from WRI’s Access Initiative and the Jamaica Environment Trust aims to promote transparency and public involvement around development projects that affect the environment and public health—projects like those planned in Goat Islands. Development Alert! proactively collects and consolidates information from different government agencies on applications for new development projects, obtaining this information through requests made using the country’s Access to Information Act. The free, mobile-friendly website plots recently approved or proposed large-scale development projects on an interactive map and acts as a hub for data and information about these projects. The map includes overlays of the boundaries of protected areas, fisheries, forest reserves, and land cover so users can easily see which projects are located in environmentally sensitive areas. Types of development projects featured include mining and quarrying; water management, treatment, and sanitation; housing developments; transportation systems and highways; tourism projects like hotel construction; hazardous waste; and more. Through the site, users can:
- View proposed and approved projects and learn about the potential impact of developments happening in their area
- Report a development they’ve seen in their neighborhood to help increase awareness about new projects, and
- Get involved by commenting on a development and voicing their concerns. The website allows users to email public authorities directly and provides details about scheduled public hearings.
A Clearer Picture of Development in Jamaica
In Jamaica, Development Alert! currently identifies 32 projects that are likely to have significant health, environmental, social, or cultural impacts, including four projects classified as high impact. Of these, 11 are located in or around protected areas. Development Alert! shows, for example, that the trans-shipment port in Goat Islands is not only within the Portland Bight Protected Area, but is also located within a fishery—the Galleon Harbour Nursery—and the Great Goat Island forest reserve. The fishery acts as a critical habitat for rebuilding fish populations and safeguarding marine resources, while the forest reserve protects the biodiversity found within these natural and nationally important ecosystems. Users can click on the project to see that CHEC submitted an application on January 1, 2014 to conduct a geotechnical survey, and that the government has already approved this survey through the grant of a beach license. The license allows the company to investigate the suitability of the area, including the bearing capacity of the soil and rock, by conducting a survey of the “foreshore and floor of the sea at Galleon Harbour.” As the map shows, this area is protected as a Special Fisheries Conservation Area. The survey is done through the drilling of 27 boreholes on and offshore. By signing up for alerts, posting comments, or emailing the government agency listed, anyone can voice their concerns about the Goat Islands project.
Shedding Light on Development and Empowering Communities
Development Alert! aims to bring an unprecedented level of transparency and participation to energy, transportation, mining, and other types of development projects in Jamaica. It will help shed light on potentially harmful projects, and provides resources to ensure the public can understand their rights to participate in decisions about their country’s development. Strengthening the involvement of those most affected by development decisions can lead to better, more inclusive decision-making. Over the coming months, the Access Initiative hopes to launch similar platforms in other countries. Visit developmentalert.org to explore the tool and learn more.