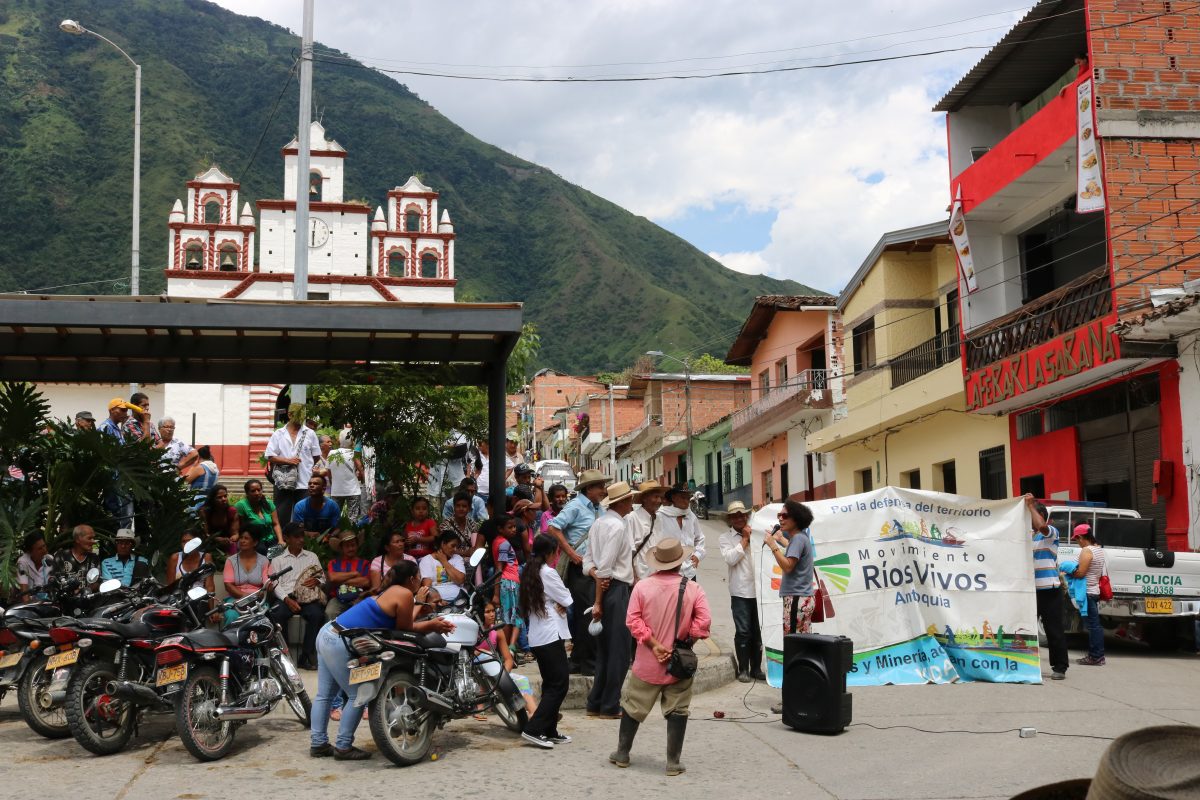
En un pintoresco pueblo situado en las colinas colombianas, Isabel Zuleta toma la palabra frente a una multitud. La policía, vestida en uniforme militar, los respalda mientras Zuleta habla sobre el derecho al agua, las preocupaciones de la comunidad sobre nuevos diques en el río Cauca, el cual usan para la pesca y otras necesidades, y las inundaciones que ha causado la represa hidroeléctrica de Hidroituango. Muchos temen que los funcionarios del gobierno estén ignorando sus preocupaciones y solicitudes de compensación.
Aunque esta manifestación y las tantas otras que Zuleta ha organizado han sido pacíficas, su trabajo no es sin conflicto. Como líder de Movimiento Ríos Vivos, un grupo dedicado a proteger los ríos de Colombia, organiza foros públicos para que las comunidades puedan expresar sus preocupaciones en relación a represas y minas. También hace lobby con el gobierno para que éste divulgue información sobre los efectos ambientales de este tipo de proyecto y organiza protestas pacíficas. Por su trabajo en defensa de las comunidades y el medio ambiente, Zuleta ha recibido numerosas amenazas de muerte. Otros miembros de Movimiento Ríos Vivos han sufrido difamación, hostigamiento y vigilancia. Hace solo unos años, dos activistas del grupo fueron asesinados.
La violencia contra los defensores del medio ambiente es prevalente no solo en Colombia, que se encuentra entre los tres países con mayor número de asesinatos de defensores, sino en todo el mundo. En 2017, casi cuatro defensores ambientales fueron asesinados por semana en su empeño por proteger sus tierras, su fauna y sus recursos naturales. América Latina es la región más peligrosa—más del 60 por ciento de asesinatos de defensores en 2016 ocurrieron en sus pueblos remotos o en las profundidades de sus bosques tropicales—mientras que las amenazas contra defensores ambientales están creciendo en el Caribe también.
Negociaciando un acuerdo jurídicamente vinculante para mejorar la democracia ambiental y proteger a los defensores
A medida que un creciente número de organizaciones luchan para elevar el perfil de los defensores ambientales y demandar que los gobiernos tomen medidas para reducir la violencia en su contra, gobiernos y grupos de la sociedad civil de América Latina y el Caribe están negociando el Acuerdo Regional sobre Acceso a la Información, Participación Pública y Acceso a la Justicia en Asuntos Ambientales, también conocido como LAC P10. Si se adopta como un acuerdo jurídicamente vinculante, requerirá que los gobiernos establezcan nuevas normas para alcanzar el Principio 10, conocido como el principio de democracia ambiental de la Declaración de Río sobre el Medio Ambiente y el Desarrollo. Estas normas aumentarían el acceso de las personas a la información ambiental (como datos de contaminación del agua o concesiones mineras), mejorarían su capacidad para participar en la toma de decisiones ambientales y les ayudarían a exigir que compañías y otros intereses rindan cuentas por acciones que perjudican a comunidades y el medioambiente.
El LAC P10 también incluye requisitos que los gobiernos protejan a las personas que buscan participar en los procesos de toma de decisiones sobre infraestructura, reduciendo así los riesgos que enfrentan los defensores ambientales. Estas estipulaciones innovadoras incluyen:
- Garantizar un entorno seguro para las personas y organizaciones que promueven y defienden los derechos humanos en asuntos ambientales, para que estén libres de amenazas, restricciones e inseguridad;
- Tomar medidas para reconocer, proteger y promover todos los derechos de los defensores ambientales; e
- Implementar medidas para prevenir, investigar y sancionar ataques, amenazas o intimidaciones contra defensores ambientales.
Desde que Chile inició las negociaciones del LAC P10 hace más de seis años, más de 20 países se han sumado al proceso. Del 28 de febrero hasta el 4 de marzo de 2018, estos países se reunirán una vez más en Costa Rica para finalizar los términos y decidir de una vez por todas si el acuerdo será legalmente vinculante.
El actual borrador propone que al menos ocho países deberán ratificar el acuerdo para que éste entre en vigor. Será fundamental que los gobiernos que previamente indicaron interés en un acuerdo vinculante firmen el tratado lo antes posible para incentivar a las otras naciones. Organizaciones de la sociedad civil de toda la región están solicitando a líderes regionales, incluyendo Brasil y Argentina, para que apoyen el acuerdo. Si las negociaciones son insuficientes, el LAC P10 no será jurídicamente vinculante, convirtiéndose en poco más de una guía voluntaria que los países podrán implementar—o no.
El acuerdo es especialmente importante en Brasil, Guatemala, México, Honduras, Perú y Colombia, que han sido algunos de los países más peligrosos para los defensores del medio ambiente y la tierra en los últimos años.
Que una persona más muera por proteger el medio ambiente es demasiado. Es hora de que los países den un paso adelante en la defensa de los defensores.